
Overview
Cloud computing helps youth-led projects by removing traditional barriers like high upfront costs and technical complexity. Young teams gain immediate access to professional-grade tools through pay-as-you-go pricing, enabling real-time collaboration across locations without expensive hardware.
The technology scales automatically with project needs, and major providers offer substantial free credits and educational programs specifically for students and nonprofits. This means a student group can launch a social impact initiative, tech startup, or community project using the same infrastructure that powers global corporations—often at little to no initial cost.
Core Benefits of Cloud Computing for Youth-Led Projects
1. Low-Cost Access to Professional Tools
The biggest advantage cloud computing offers is eliminating the need for large capital investments. Traditional IT infrastructure requires thousands of dollars in servers, software licenses, and cooling systems before you could even start building.
With cloud services, you pay only for what you use. If your team needs storage for three months during a project phase, you pay for three months. When the project ends or scales down, so do your costs.
Major providers offer extensive free tiers designed specifically for youth teams:
- Google for Startups provides up to $200,000 in credits over two years for early-stage ventures
- AWS Activate offers up to $100,000 in cloud credits plus technical mentorship
- Microsoft Azure for Students gives $100 annually without requiring a credit card
- GitHub Student Developer Pack includes free professional tools and cloud credits
These programs recognize that youth-led initiatives often start with minimal funding and operate from shared spaces rather than established offices. The pay-as-you-go model shifts technology spending from a fixed cost to a variable expense that aligns with actual usage.

2. Real-Time Collaboration Across Locations
Cloud platforms solve a fundamental challenge for youth teams: members are rarely in the same physical location. Students attend different schools, volunteers live in different cities, and remote contributors join from various time zones.
Cloud-based tools like Google Workspace, Slack, and cloud-hosted project management platforms let teams work on the same files simultaneously. Version control happens automatically—no more emailing attachments back and forth or wondering which file is the latest.
When a team member in Kenya uploads research data, a developer in Brazil can access it instantly. Changes sync in real-time, and built-in communication features keep everyone aligned without requiring separate email threads or messaging apps.
This becomes critical during time-sensitive phases like fundraising campaigns, product launches, or community events where coordination needs to happen quickly across distributed teams.
3. Scalability Without Technical Expertise
Youth projects often experience unpredictable growth patterns. A community initiative might suddenly attract media attention, or a student app could go viral on campus. Traditional infrastructure would require advance planning, hardware purchases, and technical expertise to handle traffic spikes.
Cloud computing handles this automatically. If your website receives 100 visitors on Monday and 10,000 on Tuesday, cloud hosting distributes the load across multiple servers to keep everything running smoothly. When traffic drops back to normal, resources scale down—and so does your bill.
This elasticity works in both directions. During slower periods like summer breaks or project pauses, teams can reduce their cloud usage without being locked into paying for unused capacity.
The platform provider also handles all maintenance tasks: security updates, hardware replacements, and software patches happen in the background. Small teams can redirect their limited technical resources toward building features and analyzing impact data rather than managing servers.
4. Access to Advanced Technology
Cloud platforms democratize access to tools that were previously exclusive to well-funded enterprises. Youth teams can now use artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics without specialized equipment or data science PhDs.
Cloud-hosted AI platforms allow non-technical founders to build predictive models, process natural language, or implement computer vision features. Low-code and no-code platforms use visual interfaces and pre-built components, letting students from business or design backgrounds prototype ideas without waiting for a full engineering team.
Real examples show the impact: Comet, a remote talent marketplace, was built entirely on a no-code platform by a non-technical founder and scaled to over $800,000 in monthly revenue. Teal, a career navigation platform, used similar tools to raise $5 million in funding.

Getting Started: Practical First Steps
Step #1: Identify Your Project Needs
Start by defining what you're actually building. Are you creating a website, managing a database, collaborating on documents, or developing a mobile app? Different projects require different cloud services.
List your team size and expected growth. A five-person student group has different needs than a 50-person community initiative. Estimate your project timeline—a three-month pilot needs a different approach than a multi-year program.
Be specific about required tools: file storage, video conferencing, project management, development environments, or data analytics. This prevents paying for services you don't need while missing critical features.
Step #2: Choose the Right Platform
Compare free tier offerings across major providers. Google, Amazon, and Microsoft each have strengths in different areas. AWS excels at development tools, Google offers strong collaboration features, and Microsoft integrates well with educational institutions.
Check if your school or nonprofit status qualifies you for educational discounts or extended credits. Many providers give students access to premium features that would normally cost hundreds per month.
Start with a small pilot. Choose one project component—like hosting a simple website or managing team documents—and test the platform before committing your entire infrastructure.
Step #3: Set Up Team Workflows
Clear workflows prevent chaos as your project grows. Assign specific roles: who manages billing, who approves new tool additions, who handles security settings.
Create shared folders with clear naming conventions. Use formats like "ProjectName_ComponentType_Version_Date" so files stay organized as they multiply.
Schedule regular check-ins—weekly during active phases, monthly during maintenance—to review what's working and what needs adjustment. Document your processes so new team members can get up to speed quickly.
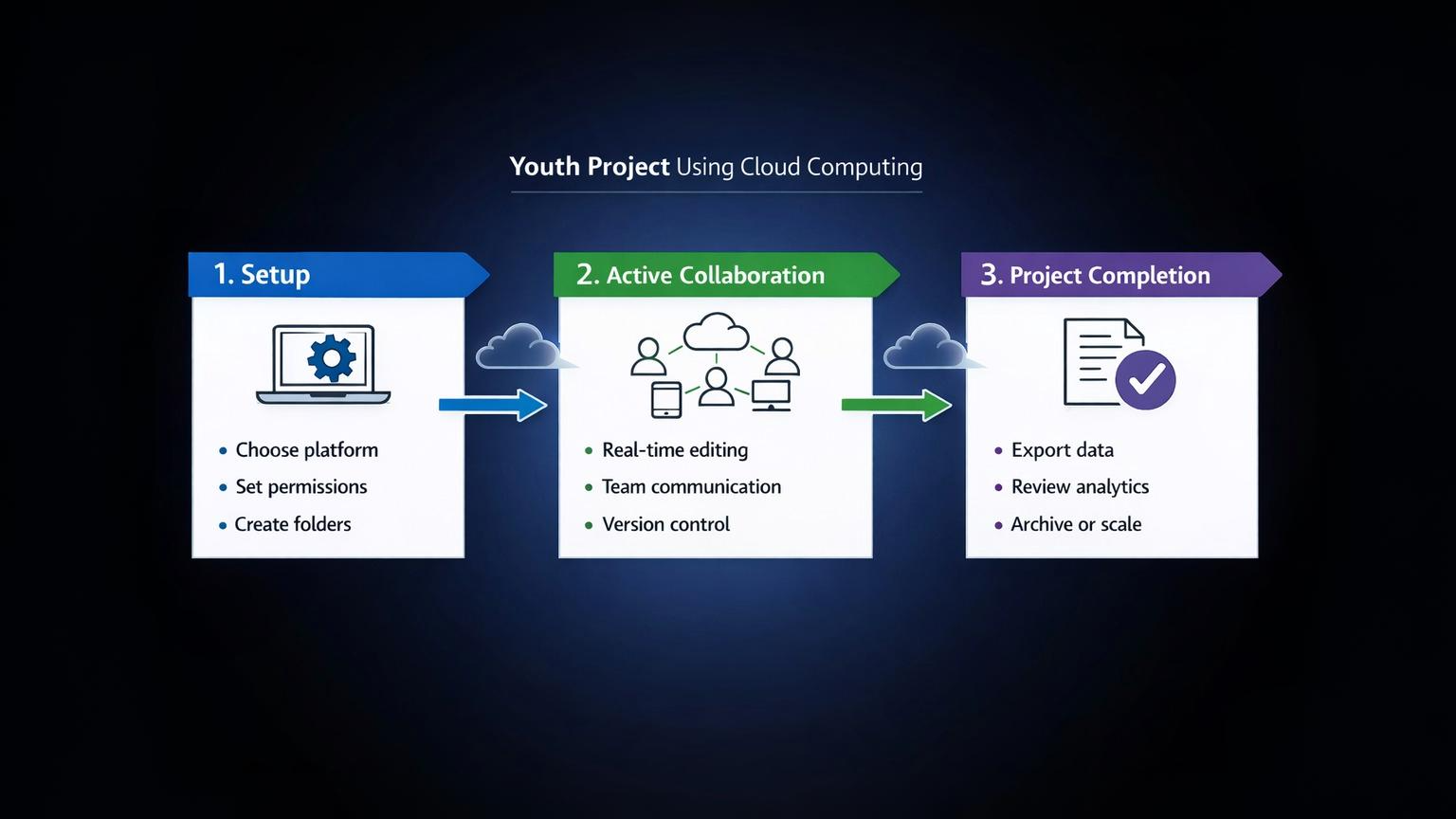
Common Mistakes Youth Teams Make With Cloud Tools
Mistake #1: Not Setting Budget Alerts
Free tiers and credits can create a false sense of unlimited resources. Teams often forget to set spending limits and receive surprise bills when they exceed free usage thresholds.
Most cloud providers offer budget alerts that notify you when spending approaches a certain amount. Set these alerts at multiple levels—like 50%, 75%, and 90% of your limit—to catch overages before they become problems.
Document which team members have permission to spin up new resources, and review usage weekly during active development phases.
Mistake #2: Poor Access Management
Sharing one admin password across the entire team seems convenient but creates serious security risks. When team members graduate, leave the project, or change roles, that shared password remains active.
Use role-based permissions instead. A content volunteer needs different access than a developer who manages infrastructure. Cloud platforms include built-in identity management that lets you grant specific permissions and revoke them instantly when someone leaves.
Enable two-factor authentication for all accounts, especially those with billing or administrative access.
Mistake #3: Ignoring Data Backup Policies
A common misconception is that "cloud storage" automatically means "backed up forever." Cloud providers protect against hardware failures, but they don't automatically create separate backup copies of your data.
If someone accidentally deletes a critical file or a misconfiguration wipes data, you need your own backup strategy. Set up automated exports to a different storage location, or use versioning features that save multiple copies of files over time.
Review your provider's terms carefully. Understand their data retention policies, what happens if your account is suspended, and how long you have to recover deleted information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can youth-led projects use cloud computing for free?
Yes, through multiple programs. Educational institutions often provide free access to cloud platforms for students. The GitHub Student Developer Pack includes cloud credits and professional tools at no cost. Provider-specific programs like AWS Activate, Google for Startups, and Azure for Students offer credits ranging from $100 to $200,000 depending on your project type and stage.
Free tiers typically cover basic needs like file storage, website hosting, and development environments. Nonprofits can apply for specialized grants that provide both cash funding and cloud credits specifically for social impact projects.
2. What happens if our project exceeds free tier limits?
Most platforms send notifications before you hit spending thresholds. You'll typically receive warnings at 75%, 90%, and 100% of your limit. Some providers offer grace periods where you can upgrade or reduce usage before billing starts.
Set up budget alerts immediately. Most platforms allow you to cap spending at a specific amount, preventing runaway costs. If you're approaching limits, review your usage dashboard to identify what's consuming resources and adjust accordingly.
3. Do we need technical skills to use cloud platforms?
Basic cloud services like file storage and collaboration tools require minimal technical knowledge—if you can use email, you can use these features. More advanced services like development platforms and databases need some learning, but providers offer free tutorials and certification programs.
Low-code and no-code platforms specifically target non-technical users. These use visual interfaces where you drag and drop components instead of writing code. Youth teams have built million-dollar businesses using these tools without formal programming backgrounds.
4. Is our project data safe in the cloud?
Major cloud providers use enterprise-grade security that most small teams couldn't afford independently: data encryption, regular security audits, and compliance certifications. Your data typically receives better protection than if you stored it on personal laptops or external drives.
However, security also depends on your team's practices. Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and implement proper access controls. Avoid sharing admin credentials and remove access immediately when team members leave.
5. How do cloud tools help teams working in different time zones?
Cloud platforms enable asynchronous collaboration. Team members work on their own schedule without needing everyone online simultaneously. Changes sync automatically, so when someone in Europe updates a document, a teammate in Asia sees those changes when they log in later.
Version history shows who made which changes and when, preventing confusion. Built-in commenting and notification features keep everyone informed without requiring real-time meetings. Teams can schedule automated reports or use project management tools that show progress regardless of when individual members contribute.
Final Summary
Cloud computing transforms youth-led projects by removing the financial and technical barriers that traditionally limited young innovators. With pay-as-you-go pricing, professional tools become accessible to student groups and community initiatives without upfront investment. Real-time collaboration features connect distributed teams, while automatic scaling handles growth without requiring technical expertise.
The ecosystem of educational credits, free tiers, and nonprofit grants means most youth projects can start and scale with minimal costs. Whether you're building a social impact initiative, launching a startup, or managing a community program, cloud platforms provide the infrastructure that lets you focus on your mission rather than managing technology.
Start small—choose one tool or platform, test it with your team, and expand as you learn what works for your specific needs. The barrier to entry has never been lower.
Published by URX Media, a platform focused on learning and explaining digital marketing, business and technology concepts through simple, accurate breakdowns.
📚Related Articles

What Is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) Business Model and How Does It Work?
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based delivery system where users access applications through subscription payments rather than purchasing and installing software locally.

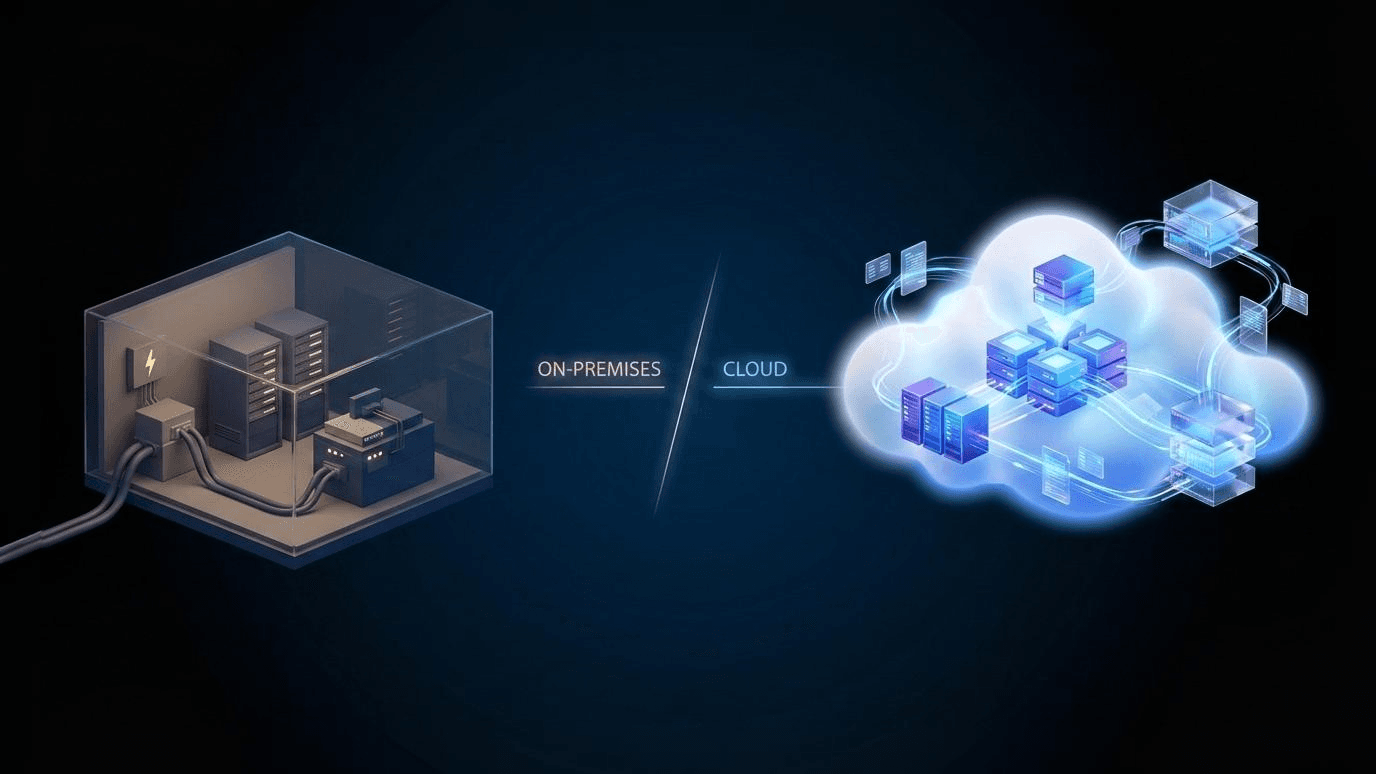
How Is Cloud Computing Different From Traditional IT Infrastructure?
Cloud computing delivers computing resources—servers, storage, and software—over the internet on demand. You don’t own the hardware; you rent what you need and scale usage up or down as required. Traditional IT infrastructure relies on physical servers and systems that a business owns, hosts on-site or in a private data center, and manages internally.
Showing 3 of 4 posts